Molsoft's Technology |
Success Stories | Publications
MolSoft develops cutting-edge technology and proprietary algorithms for molecular modeling, with applications in protein and small-molecule structure prediction, docking, structure-based drug design, molecular visualization and animation, bioinformatics, cheminformatics, and laboratory information management systems.
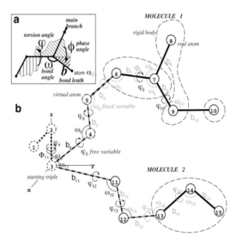 MolSoft's ICM software package is based on the internal coordinates (IC) representation of molecular objects that naturally reflects the covalent bond geometry of molecules ( Abagyan et al., 1994 ). Unlike simple Cartesian coordinates, IC variables consist of covalent bond lengths and angles, torsion angles and six positional coordinates of a molecular object. Because of chemical bond rigidity, most molecular objects can be accurately represented by free torsion variables while keeping covalent bond coordinates fixed. This dramatically reduces the number of free variables in the system without sacrificing accuracy, while improving convergence time for conformational optimizations at least 1000-fold. Moreover, further reduction of free variable space and system complexity in ICM can be achieved by effectively freezing IC variables in more rigid or less important parts of the model. When carefully applied and validated, such complexity reductions reduce unnecessary noise in the modeling system and enable faster and more reproducible energy optimizations.
MolSoft's ICM software package is based on the internal coordinates (IC) representation of molecular objects that naturally reflects the covalent bond geometry of molecules ( Abagyan et al., 1994 ). Unlike simple Cartesian coordinates, IC variables consist of covalent bond lengths and angles, torsion angles and six positional coordinates of a molecular object. Because of chemical bond rigidity, most molecular objects can be accurately represented by free torsion variables while keeping covalent bond coordinates fixed. This dramatically reduces the number of free variables in the system without sacrificing accuracy, while improving convergence time for conformational optimizations at least 1000-fold. Moreover, further reduction of free variable space and system complexity in ICM can be achieved by effectively freezing IC variables in more rigid or less important parts of the model. When carefully applied and validated, such complexity reductions reduce unnecessary noise in the modeling system and enable faster and more reproducible energy optimizations.
 Docking (in ICM-Pro) and Screening (in ICM-Pro + VLS) provides a unique set of tools for accurate ligand-protein docking,
peptide-protein docking, and protein-protein docking. The ICM-Pro desktop modeling GUI interface offers a step-by-step docking menu or can be scripted for large-scale docking and screening.
More...
Docking (in ICM-Pro) and Screening (in ICM-Pro + VLS) provides a unique set of tools for accurate ligand-protein docking,
peptide-protein docking, and protein-protein docking. The ICM-Pro desktop modeling GUI interface offers a step-by-step docking menu or can be scripted for large-scale docking and screening.
More...
 MolSoft’s RTCNN (Radial and Topological Convolutional Neural Network) is a hybrid neural-network-based scoring function designed for ligand–receptor docking. It combines 2D topological graph convolutions and 3D radial convolutions to learn interaction patterns directly from structural data, eliminating the need for traditional physics-based energy terms. Trained on high-quality protein–ligand complexes and decoys, RTCNN excels at distinguishing native-like binding poses, outperforming many conventional scoring functions on benchmarks such as CASF-2016. In virtual screening, it complements MolSoft’s physics-based Score; the recommended workflow is to prioritize ligands that score well by both criteria, since RTCNN penalizes steric clashes less harshly and emphasizes native interaction patterns. More...
MolSoft’s RTCNN (Radial and Topological Convolutional Neural Network) is a hybrid neural-network-based scoring function designed for ligand–receptor docking. It combines 2D topological graph convolutions and 3D radial convolutions to learn interaction patterns directly from structural data, eliminating the need for traditional physics-based energy terms. Trained on high-quality protein–ligand complexes and decoys, RTCNN excels at distinguishing native-like binding poses, outperforming many conventional scoring functions on benchmarks such as CASF-2016. In virtual screening, it complements MolSoft’s physics-based Score; the recommended workflow is to prioritize ligands that score well by both criteria, since RTCNN penalizes steric clashes less harshly and emphasizes native interaction patterns. More...
 GINGER is a GPU-accelerated conformer generator developed by MolSoft, designed to rapidly produce diverse, low-energy 3D conformations of molecules with high accuracy and efficiency. Integrated into ICM-Pro and ICM-Chemist-Pro, it combines a neural network-based approach with fast force-field refinement, enabling the processing of over 10 million compounds per day on a single GPU. GINGER is highly scalable, memory-efficient, and robust—successfully handling over 99.9% of compounds. It generates fewer conformers while maintaining accuracy, making it ideal for large-scale virtual screening workflows and compatible with MolSoft tools like RIDE and RIDGE. More...
GINGER is a GPU-accelerated conformer generator developed by MolSoft, designed to rapidly produce diverse, low-energy 3D conformations of molecules with high accuracy and efficiency. Integrated into ICM-Pro and ICM-Chemist-Pro, it combines a neural network-based approach with fast force-field refinement, enabling the processing of over 10 million compounds per day on a single GPU. GINGER is highly scalable, memory-efficient, and robust—successfully handling over 99.9% of compounds. It generates fewer conformers while maintaining accuracy, making it ideal for large-scale virtual screening workflows and compatible with MolSoft tools like RIDE and RIDGE. More...
 CombiRIDGE is a GPU-powered, high-throughput docking solution from MolSoft that efficiently explores massive combinatorial libraries by “growing” new molecules around a known core (anchor) fragment. The process starts with embedding the anchor in the binding site, then uses GINGER to generate full 3D conformers in situ, quickly expands R‑group possibilities, and refines poses via GPU‑driven energy minimization. Final scoring is performed using a graph neural network (RTCNN) to identify top candidates. In a demo, CombiRIDGE screened 28 billion Enamine compounds on a single RTX 4090 by generating 3D anchors (18 M in ~40 hrs), docking them (3.5 K/min over ~90 hrs), and expanding the library in just 6 hrs. A challenging test case with the drug Venetoclax reproduced the crystal pose with an RMSD of 1.07 Å. More...
CombiRIDGE is a GPU-powered, high-throughput docking solution from MolSoft that efficiently explores massive combinatorial libraries by “growing” new molecules around a known core (anchor) fragment. The process starts with embedding the anchor in the binding site, then uses GINGER to generate full 3D conformers in situ, quickly expands R‑group possibilities, and refines poses via GPU‑driven energy minimization. Final scoring is performed using a graph neural network (RTCNN) to identify top candidates. In a demo, CombiRIDGE screened 28 billion Enamine compounds on a single RTX 4090 by generating 3D anchors (18 M in ~40 hrs), docking them (3.5 K/min over ~90 hrs), and expanding the library in just 6 hrs. A challenging test case with the drug Venetoclax reproduced the crystal pose with an RMSD of 1.07 Å. More...
 The Atomic Property Field (APF) method developed by MolSoft ( Totrov 2008) is a 3D pharmacophoric potential implemented on a continuously distributed grid which can be used for ligand docking and scoring. APF can be generated from one or more high affinity scaffolds and seven properties are assigned from empiric physico-chemical components.
More...
The Atomic Property Field (APF) method developed by MolSoft ( Totrov 2008) is a 3D pharmacophoric potential implemented on a continuously distributed grid which can be used for ligand docking and scoring. APF can be generated from one or more high affinity scaffolds and seven properties are assigned from empiric physico-chemical components.
More...
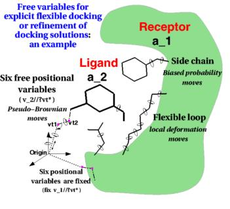
 ICM contains a selection of tools to account for pocket flexibility (induced fit) in docking and virtual screening. The importance of considering flexibility in proteins is well understood (1-3) and is an important consideration when undertaking structure-based drug design. There are three main approaches in ICM for incorporating induced fit:
More...
ICM contains a selection of tools to account for pocket flexibility (induced fit) in docking and virtual screening. The importance of considering flexibility in proteins is well understood (1-3) and is an important consideration when undertaking structure-based drug design. There are three main approaches in ICM for incorporating induced fit:
More...
 The ICM Ligand Editor is an intuitive graphical interface for ligand optimization and drug design. The editor was developed in close collaboration with Medicinal Chemists at Novartis and designed for ease of use and high accuracy ligand modeling. The ligand editor is available in ICM-Pro and ICM-Chemist-Pro.
More...
The ICM Ligand Editor is an intuitive graphical interface for ligand optimization and drug design. The editor was developed in close collaboration with Medicinal Chemists at Novartis and designed for ease of use and high accuracy ligand modeling. The ligand editor is available in ICM-Pro and ICM-Chemist-Pro.
More...
 MolSoft and Novartis have developed a new desktop modeling and communication environment for drug discovery called FOCUS based on MolSoft's Internal Coordinate Mechanics (ICM) software. The FOCUS platform is described in a publication in the ACS Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling (see Stiefl et al 2015). FOCUS is a platform that helps users communicate chemical and structural data, develop new ideas and support decision making during the drug design cycle. FOCUS can be integrated into an informatics and high performance computing environment giving the user a single interface to many capabilities.
More...
MolSoft and Novartis have developed a new desktop modeling and communication environment for drug discovery called FOCUS based on MolSoft's Internal Coordinate Mechanics (ICM) software. The FOCUS platform is described in a publication in the ACS Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling (see Stiefl et al 2015). FOCUS is a platform that helps users communicate chemical and structural data, develop new ideas and support decision making during the drug design cycle. FOCUS can be integrated into an informatics and high performance computing environment giving the user a single interface to many capabilities.
More...
 RIDE is a fast 3D molecular similarity search method based on Atomic Property Fields, developed at MolSoft. RIDE searches databases of compound conformers for molecules that are isosteric to the query, i.e. have similar 3D configurations and distributions of atomic properties.RIDE is available in the ICM-Pro + VLS package.
More...
RIDE is a fast 3D molecular similarity search method based on Atomic Property Fields, developed at MolSoft. RIDE searches databases of compound conformers for molecules that are isosteric to the query, i.e. have similar 3D configurations and distributions of atomic properties.RIDE is available in the ICM-Pro + VLS package.
More...
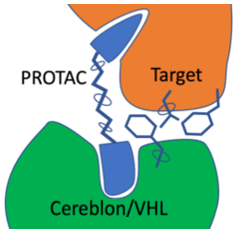 Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD) is an approach that is attracting substantial interest for modulating challenging drug
targets. A major class of TPDs are Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera protein degraders (PROTACs). PROTACs are heterobifunctional molecules where two ligands are joined by linker. One ligand recruits the target and the other recruits and binds an E3 ubiquitin ligase. This interaction induces ubiquitylation of the target and degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system, the PROTAC is then recycled.
More...
Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD) is an approach that is attracting substantial interest for modulating challenging drug
targets. A major class of TPDs are Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera protein degraders (PROTACs). PROTACs are heterobifunctional molecules where two ligands are joined by linker. One ligand recruits the target and the other recruits and binds an E3 ubiquitin ligase. This interaction induces ubiquitylation of the target and degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system, the PROTAC is then recycled.
More...
 MolSoft has a long history of developing methods for RNA drug discovery. The first ever successful virtual screen was against an RNA-protein interaction (tat-TAR). RNA drug discovery companies such as Arrakis Therapeutics, Novartis and Nymirum have published success stories using MolSoft ICM. More...
MolSoft has a long history of developing methods for RNA drug discovery. The first ever successful virtual screen was against an RNA-protein interaction (tat-TAR). RNA drug discovery companies such as Arrakis Therapeutics, Novartis and Nymirum have published success stories using MolSoft ICM. More...
 All ICM products can be run on the cloud - AWS, Google Cloud or Azure. You can read about the World's Largest ever virtual screen resulting in 3 new lead compounds from Novartis and a 680 million structure-based screen performed in 24 hours by USC. More...
All ICM products can be run on the cloud - AWS, Google Cloud or Azure. You can read about the World's Largest ever virtual screen resulting in 3 new lead compounds from Novartis and a 680 million structure-based screen performed in 24 hours by USC. More...