Google Search the Manual:
Keyword Search:
| Prev | ICM User's Guide 5.1 Convert to ICM Object | Next |
[ Load a Protein Structure | Convert | Convert Chemical ]
| Available in the following product(s): ICM-Browser | ICM-Browser-Pro | ICM-Pro | ICM-Chemist |
5.1.1 Load a Protein Structure |
There are a couple of ways to read into ICM a protein structure.
- Search the PDB using the Search Tab.
- Load in a PDB file that you have saved on your computer using File/Open.
5.1.2 Converting PDB Files Into ICM Objects |
To perform any energy-based calculation in ICM (for example, docking, displaying hydrogen bonds, or displaying electrostatic or binding property surfaces), a protein or small molecule must first be converted into an ICM object.
The convertObject macro converts a non-ICM structure, such as a PDB file,
into a fully defined ICM object suitable for energy-based calculations.
This conversion produces a complete all-atom model with assigned atom types,
formal and partial charges, and an internal-coordinate representation.
An ICM object is required for docking, energy evaluation, hydrogen-bond analysis,
and electrostatic or binding property surface calculations.
During conversion, ICM applies a series of automated refinement steps to ensure the structure is chemically and energetically consistent. Missing side-chain atoms for known residues may be added, atom types and charges are assigned using ICM and MMFF rules, and alternative atom positions are resolved. Missing backbone segments or loops are not built. The original input object is preserved unless explicitly replaced by user options.
Depending on the selected arguments, convertObject can delete or retain
water molecules, optimize hydrogen placement, evaluate histidine protonation states,
flip Asn and Gln side chains, adjust cysteine states near metal ions, and assign ligand
charge states using MolSoft's pKa model. Additional string options allow control over
water handling, ligand tautomer optimization, and atom name correction. All changes
made during conversion are reported in the command-line shell and can be reviewed
by the user.
See the command line manual for a more complete description of what the conversion process does.
| NOTE: Before converting a protein structure to an ICM object make sure that the chemicals contained within the structure (e.g. ligands) are correct. If an error is found you can edit the ligand as described here. |
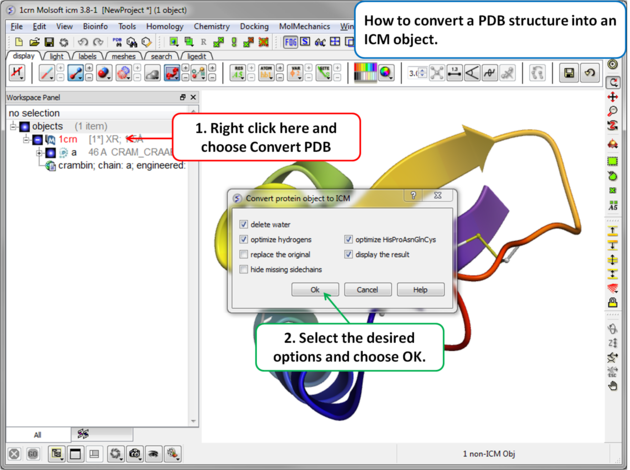
To convert a PDB structure into an ICM object follow the steps shown below:
- Right click on the name of the protein you wish to convert in the ICM Workspace.
- A dialog box will be displayed as shown below.
- To delete the water molecules select Delete Waters, loose waters are defined as those not making any h-bonds with the ligand or protein, tight waters are those making 3 or more h-bonds.
- To optimize hydrogen atoms (recommended) select Optimize Hydrogens. This option performs global optimization of hydrogens to find the best hydrogen bonding network.
- To optimize the orientation of His, Pro, Asn, Gln, Cys residues then choose optimizeHisProAsnGlnCys. The following residues will be further optimized: His - three protonation states and two rotations will be tried and the residue will be renamed according to its subtype: hie (epsilon tautomer) or hip (+). Asn and Gln - (a 180 deg. flip will be tried). Cys - in the vicinity of Zn, Cu, Fe and Co to cym.
- To keep a copy of your PDB file uncheck the option replace original.
- The converted structure can be displayed immediately by checking display the result
- Uncheck the box hide missing side chains if you want ICM to build missing heavy atoms that are not reported in the PDB (due to the lack of density), they will be added according to the residue name and assigned zero occupancies. Check this box if you want residues missing heavy atoms to be hidden.
- Tautomer Optimize ligand tautomer. For each ligand (hetero a_H), different tautomeric forms are generated and their energies are evaluated using the "hb, vw, 14, el" terms in the context of other chains. The lowest-energy tautomer is then selected as the preferred form.
If your object is an ICM object it will display ICM next to the molecule in the ICM Workspace.

5.1.3 How to Edit and Convert a Chemical from the PDB into an ICM Object |
[ ICM Workspace | Graphical Display ]
The protein data bank has not been storing any information about covalent bond types and formal charges of the chemical compounds interacting with proteins! This oversight makes it impossible to automatically convert those molecules to anything sensible and requires your manual interactive assignment of bond types and formal charges for each compound in a pdb-entry. Therefore, if you apply the convert command to a pdb-entry with ligands, the ligands will just become some crippled incomplete molecules that can not be further conformationally optimized.
Therefore, follow these steps to convert a chemical properly from a pdb form to a correct icm object. There are two ways to do this either via the ICM Workspace (recommended) or via the Graphical Display.
5.1.3.1 Converting a Chemical from the PDB using the ICM Workspace |
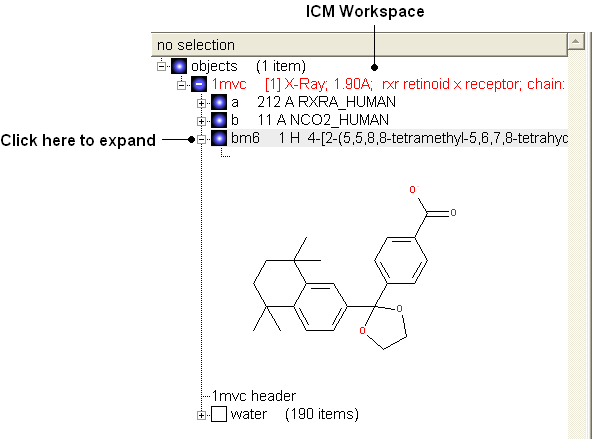
- File/Open PDB
- View the ligand in the ICM Workspace by expanding the molecule tree (see below).
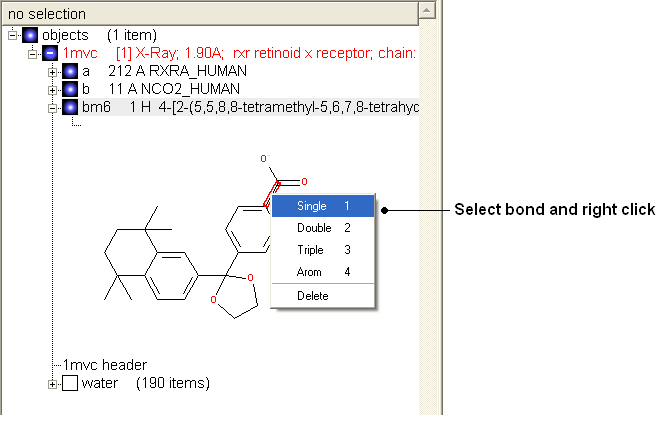
Change bond orders:
- Change the bond orders by selecting the bond (highlighted in red).
- Right click and select the desired bond as shown below.
| NOTE: Keyboard shortcuts are provided to make editing faster. |
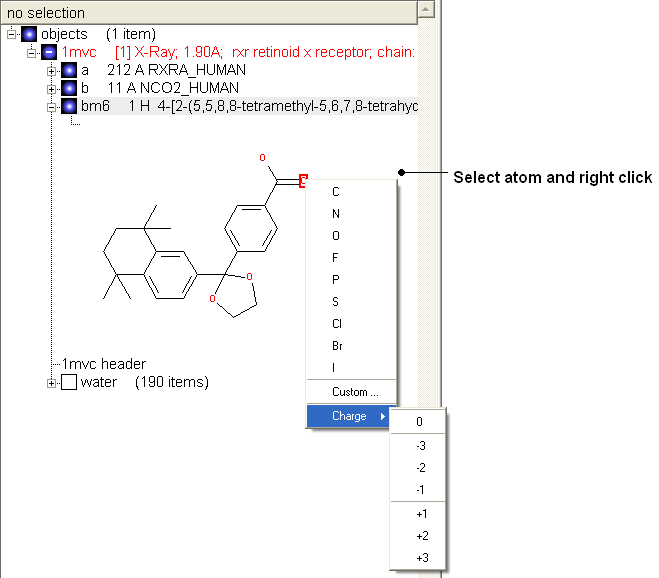
Change atom and charge:
- Change the atom or charge by selecting the atom (highlighted in red).
- Right ckick and select the desired atom or charge as shown below.
| NOTE: Keyboard shortcuts are provided to make editing faster. |
Convert to 3D in MMFF force field:
- Once you have made the changes to the ligand - right click on the name of the ligand in the ICM Workspace and select Move from Object.
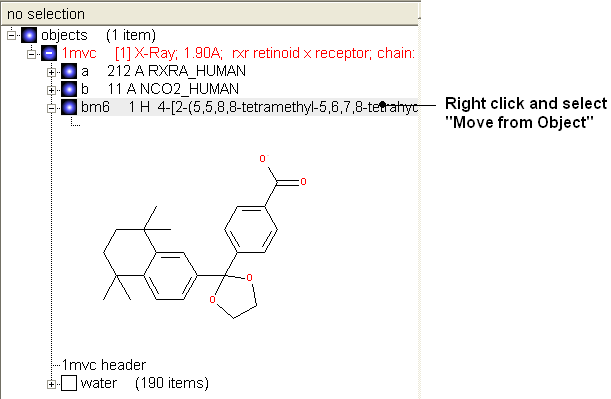
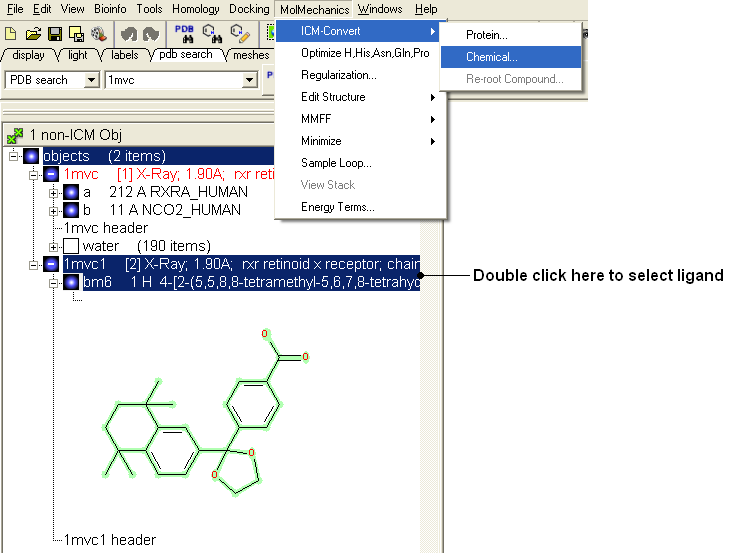
- Select the ligand by double clicking on it in the ICM Workspace.
- Select MolMechanics/ICM-Convert/Chemical
| NOTE: If you need to add an extra bond you will need to use the full molecular editor. Right click on the name of the ligand in the ICM Workspace and select Edit/Edit Compound. |
5.1.3.2 How to Convert a Chemical from the PDB using the Graphical Display |
- Display the molecule in wire chemistry style mode by right clicking on the Wire Representation button (see Wire Representation section).
To change the bond types in your ligand:
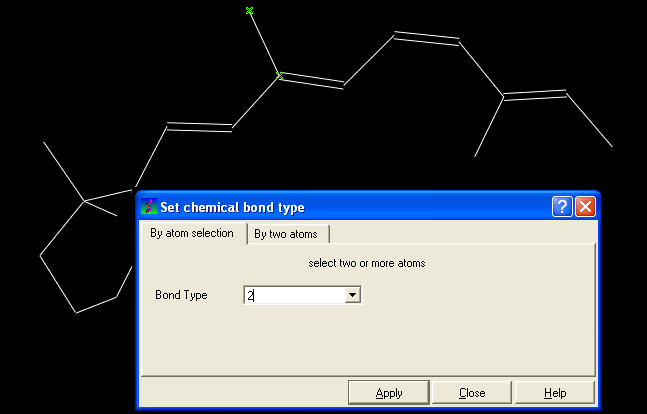
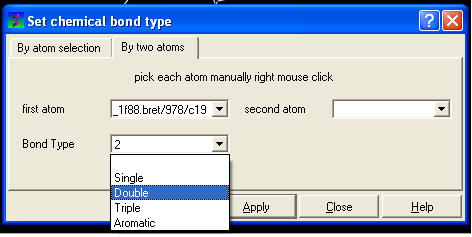
- Click on MolMechanics/Edit Structure/Set Bond Type and the Set chemical bond type data entry box will be displayed.
You can either select (see selection menu section)the atoms you wish to change graphically using the rectangular or lasoo selection button OR
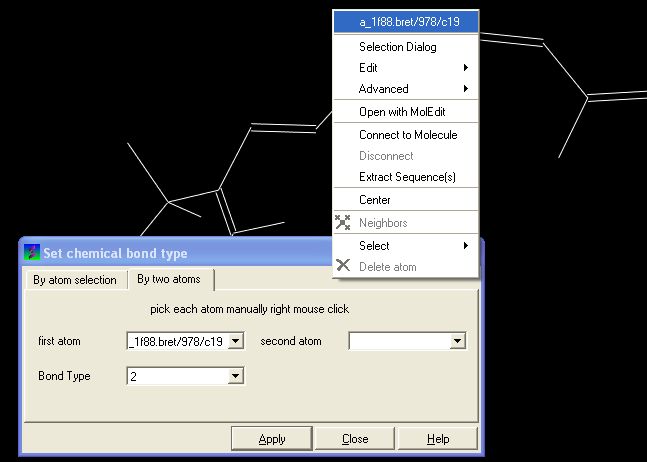
You can select the By two atoms tabs and right click on the atoms you wish to change and then selecting the atom descriptor with the left mouse button as shown below.
- Select the desired bond type either single, double, triple or aromatic.
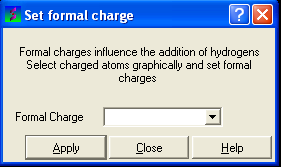
To set the formal charge of a compound:
Click on MolMechanics/Edit Structure/Set Formal Charge and then select the appropriate charge.
The final step is to convert the compound into an ICM object:
- Select the chemical (green crosses in graphical display).
- MolMechanics/ICM-Convert/Chemical
| Prev Protein Structure | Home Up | Next Pocket Display |