Google Search the Manual:
Keyword Search:
| Prev | ICM User's Guide 9.13 Predicting Change in Binding Free Energy upon Mutation | Next |
| Tutorial |
| Available in the following product(s): ICM-Pro |
This method computes the change in binding free energy of a protein complex upon mutation of a single residue.
Getting Started A PDB structure or ICM object containing the protein complex is needed. A graphical selection of the residue to be mutated is then made, the mutant amino acid (e.g., "ala" or "all" for calculation of the energy for all natural amino acids) is then selected. The energy is computed as interaction energy between two parts (each part may contain more than one protein chain). One part has to be specified, e.g., "a" or "a,b".
CalculationThe binding free energy change, ..Gbind, is computed as a difference between the free energy of mutant and wild type:
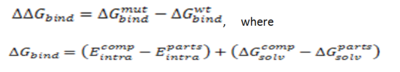
where Ecomp represents the energy of the complex, and Eparts represents the sum of the energies, internal or solvation, for each part. The energy is calculated for fixed backbone and all the side chains except those in the vicinity of the mutatable residue. Monte Carlo simulations are carried out to relieve possible atomic clashes created as a result of mutations to larger amino acid residues. "Scan Protein Interface" option allows to mutate all residues (one by one) of the Interacting Part in close contact with the second part of the complex.
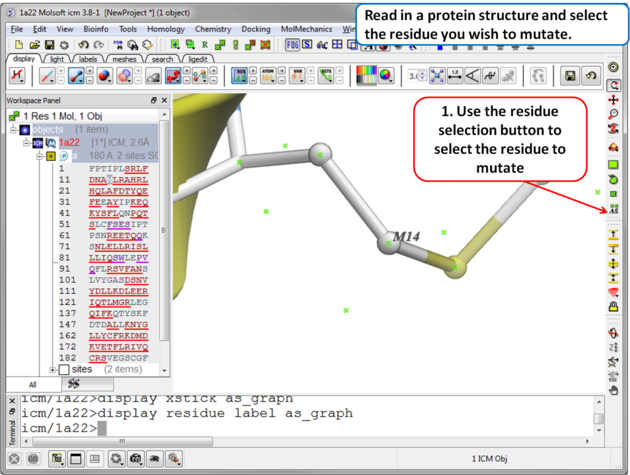 |
| Step 1 Read in the PDB file of interest and select the residue you wish to mutate. |
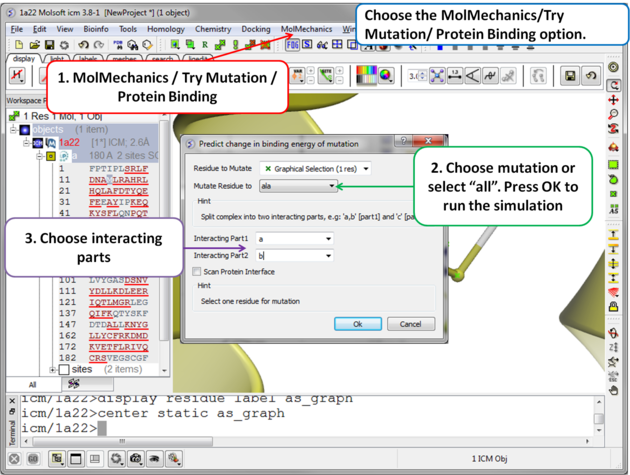 |
| Step 2 Choose the option MolMechanics/Try Mutation/ Protein Binding and a dialog box as shown above will be displayed. If you have selected a residue it should be reported in the "Residue to Mutate" box. Select a residue to mutate to from the drop down list or select "all" to try all 20 natural amino acids. One or more interacting part(s) of the protein need to be specified e.g. if chain a interacts with chain b - enter "a" as interacting chain 1 and "b" as interacting chain 2. The "Scan Protein Interface" option allows to mutate all residues (one by one) of the Interacting Part1 in close contact with the second part of the complex |
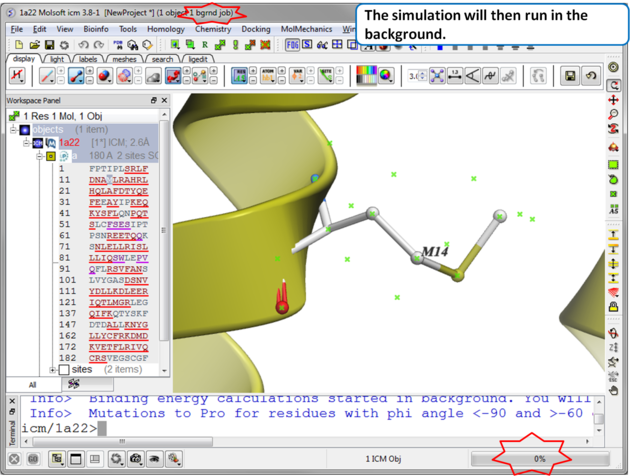 |
| Step 3 The simulation will run in the background and may take a while to finish if the option "all" or "scan protein interface" is selected. |
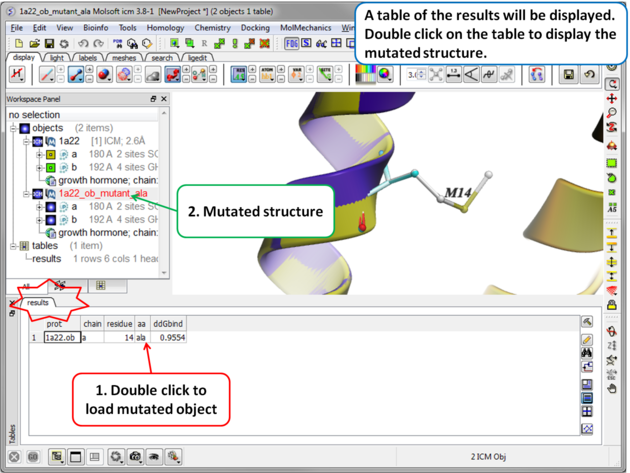 |
| Step 4 A table reporting the binding free energy in kcal/mol (ddGbind) will be displayed. Double click a row of the table to load and display the mutated structure. |
| Prev Modify Amino Acid | Home Up | Next Mutation - Protein Stability |